Dear Moon, don’t let Earth attraction destroy you.
The daily cycle of ocean tides on Earth is a known consequence of the gravitational pull exerted by the moon as it orbits the planet. But apparently, the force that keep the Moon where it is now have a more serious impact on our satellite: the force is so great that it is literally breaking and shrinking its surface.
After being in orbit for over six-years, the cameras on board the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LROC) have photographed almost three-quarters of high-resolution images of Earth’s natural satellite, and have allowed researchers to identify more than 3,200 fractures along the lunar surface, with each fracture being several kilometers long and tens of meters deep.
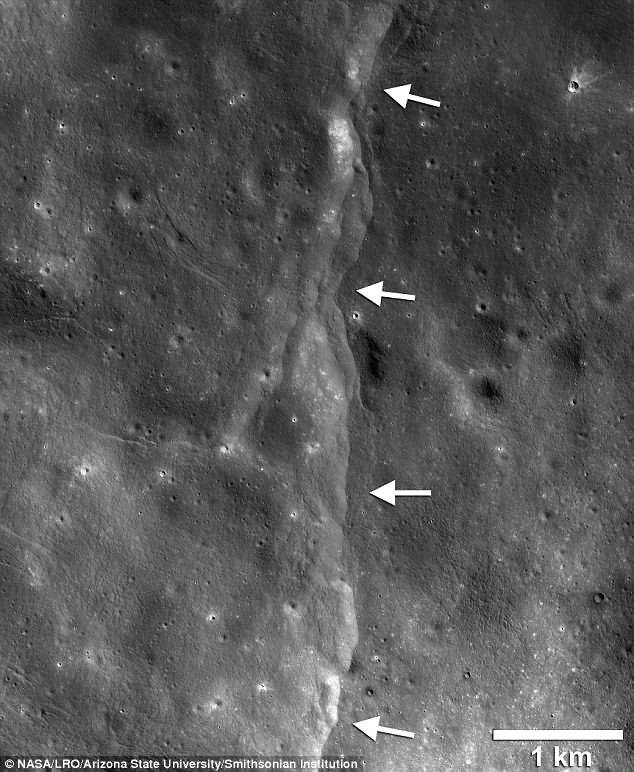
Cracks here… Cracks there…
Dr Thomas Watters, a senior scientist at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, said: ‘There is a pattern in the orientations of the thousands of faults.
Dr. Thomas R. Watters says that the overall contraction alone should generate a series of failures with no particular pattern in its guidelines, because the contraction forces have equal magnitude in all directions, yet strangely this is not what we found. Dr Watters added: when the tidal forces on the moon were superimposed on the global contraction caused by the cooling interior, the combined stresses produced cracks to form in distinct patterns.
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is NASA’s robotic spacecraft and the mission is a precursor to future human and robotic missions to the Moon by NASA. The first images from LRO were published on July 2, 2009, showing a region in the lunar highlands south of Mare Nubium. The mission was launched on June 18 2009.
John Kelly, LRO project scientist at Nasa’s Goddard Space Flight Centre in Maryland, said: ‘With LRO we’ve been able to study the moon globally in detail not yet possible with any other body in the solar system beyond Earth, and the LRO data set enables us to tease out subtle but important processes that would otherwise remain hidden.
