The cannabinoid THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) continues to be a focal point of scientific interest due to its pronounced potency and the potential implications for both therapeutic use and understanding the broader effects of cannabis. Building on the foundational knowledge of THCP’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system, recent research endeavors have sought to further delineate its properties, effects, and potential applications.
THCP, or tetrahydrocannabiphorol, is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants, known for its significant potency and potential therapeutic benefits. Discovered by Italian researchers in 2019 at the same time as its cousin, (THCB), THCP has sparked interest for its strong psychoactive effects and interaction with the endocannabinoid system, binding to CB1 and CB2 receptors more effectively than THC, suggesting a higher potency and a range of effects.
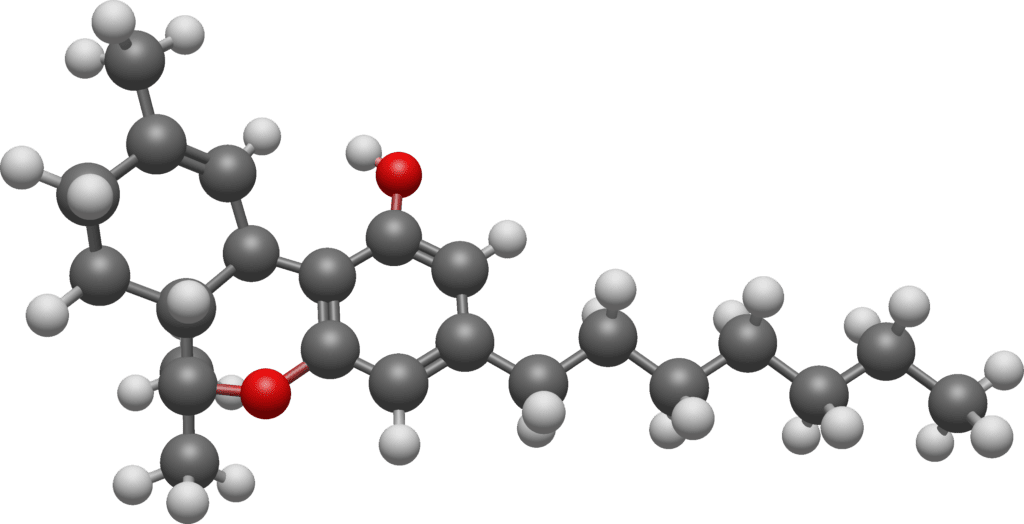
Current Insights into THCP
As research into cannabis compounds deepens, THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) has emerged as a noteworthy cannabinoid due to its unique properties. Here are the essential facts gathered about THCP:
- THCP is present in cannabis plants but only in minimal amounts.
- It is one of over 150 phytocannabinoids identified within the cannabis plant.
- Compared to delta 9 THC, THCP demonstrates a significantly higher affinity for CB1 endocannabinoid receptors, binding 33 times more effectively.
- THCP can be meticulously extracted and isolated from both marijuana and hemp sources.
Key Takeaways:
- Potency and Affinity: THCP’s enhanced binding capability with CB1 receptors suggests a potency that surpasses the well-known delta 9 THC, potentially offering more pronounced effects.
- Extraction and Isolation: Despite its scarce presence in cannabis, advanced extraction techniques allow for the isolation of THCP, making further study and potential therapeutic use possible.
- Diverse Cannabinoid Spectrum: THCP’s discovery underscores the complexity and diversity of cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, highlighting the vast potential for new discoveries within this botanical domain.
- Research and Therapeutic Potential: The unique interaction of THCP with the endocannabinoid system opens new avenues for research, particularly in understanding its impact on human health and potential therapeutic applications.

Recent Discoveries and Research on THCP
THCP was identified as a potent agonist for CB1 and CB2 receptors, with a binding affinity approximately 33 times greater than that of Δ9-THC. This discovery has prompted a deeper examination of THCP’s psychoactive effects, which are reported to be significantly more intense than those associated with traditional THC. Advanced liquid chromatography techniques have played a crucial role in isolating THCP, enabling researchers to study its unique characteristics and effects more closely (Neurogan CBD).
Potential Therapeutic Benefits
The heightened potency of THCP suggests it could have profound effects on pain relief, mood regulation, and possibly other medical conditions. Initial studies have explored THCP’s pharmacological profile, revealing its ability to induce hypomotility, analgesia, catalepsy, and decreased rectal temperature, which are indicative of its strong cannabinoid-like activity. These findings hint at THCP’s potential for developing new therapeutic agents, though further research is needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety (NCBI).
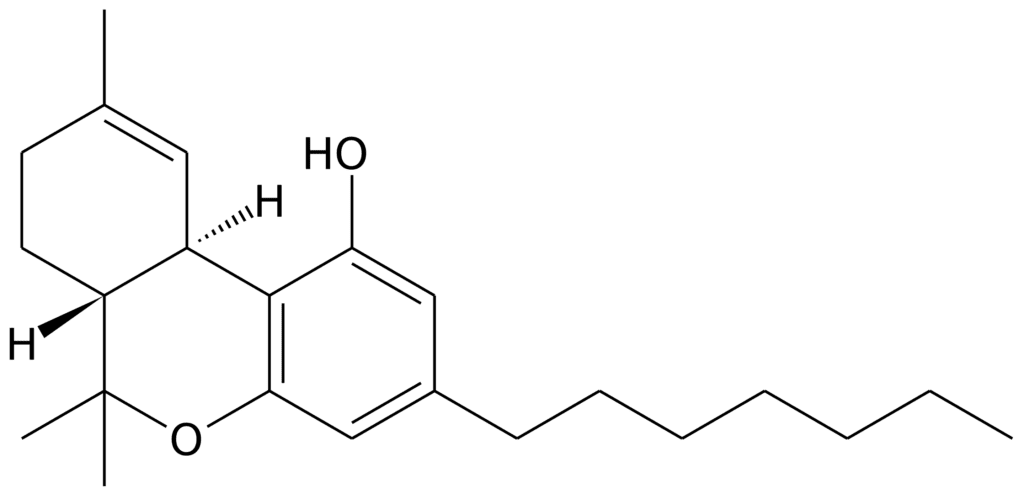
Comparative Overview of Cannabinoids in Cannabis
The cannabis plant is a complex botanical source that produces a variety of cannabinoids, each with unique properties and effects. Among these, certain cannabinoids have become more familiar due to their prevalence and the extent of research into their effects. Here’s a brief comparison of some of the more well-known cannabinoids, including the recently discovered THCP, to provide a clearer understanding of how they differ in terms of concentration, activation process, and potential benefits.
Please note, these are general estimates, and actual concentrations can vary based on the cannabis strain, growing conditions, and processing methods.
| Cannabinoid | Psychoactivity | Estimated Concentration in Cannabis | Notable Effects | Decarboxylation Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD (Cannabidiol) | No | ~15% in marijuana, 20-30% in hemp | Anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, neuroprotective | Yes |
| THC (Delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabinol) | Yes | 25-35% in marijuana, 0.3% in hemp | Psychoactive, euphoria, pain relief | Yes |
| CBG (Cannabigerol) | No | <1% | Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, neuroprotective | Yes |
| CBC (Cannabichromene) | No | <1% | Anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, promotes brain growth | Yes |
| CBN (Cannabinol) | Mildly | Increases as THC degrades, very low in fresh plant | Sedative, pain relief, anti-inflammatory | Derived from THC degradation |
| THCP (Delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) | Yes | <0.1% | Strong psychoactivity, potentially enhanced therapeutic effects | Yes |
| HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) | Yes | Not specified, synthetically modified | Similar to THC, less research available | Not applicable (synthetic) |
| THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) | No (becomes psychoactive when decarboxylated) | Predominant in raw cannabis, varies widely | Precursor to THC, anti-inflammatory | Yes |
| THC-O (THC-O-Acetate) | Yes | Synthetically derived, not naturally occurring | Potent psychoactive effects, more research needed | Not applicable (synthetic) |
| THCB (Tetrahydrocannabutol) | Yes | <0.1% | Psychoactive, less researched than THC | Yes |
Key Insights:
- Variability in Concentration: THC and CBD are present in the highest concentrations within the cannabis plant, while other cannabinoids like CBG, CBC, and THCP are found in much lower amounts.
- Psychoactivity: THC, THCP, and THCB are known for their psychoactive effects, with THCP being particularly notable for its high potency.
- Therapeutic Potential: Each cannabinoid offers distinct therapeutic benefits, from anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects to pain relief and mood regulation.
- Activation and Synthesis: Most cannabinoids require decarboxylation to become active, except for those that are synthetically derived, like HHC and THC-O, or those that are already in an active form.
This table aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the cannabinoids produced by the cannabis plant, emphasizing the importance of continued research to fully understand their effects, interactions, and potential benefits.
Safety and Potency Concerns
Given its recent discovery in 2019, there is limited research on THCP’s long-term safety and overall potency. However, scientists are conducting studies on animal models to assess its effects and potential health implications. Some studies have suggested that THCP may be effective in treating certain types of cancer, while others are investigating its usefulness in managing other health conditions. Despite these promising avenues, the need for careful dosing and further study is emphasized to ensure safe and effective use (Medical Mike’s).

THCP Gummies
One of the most popular ways to experience the benefits of THCP is through gummies, offering a convenient and enjoyable method of consumption. Shayana Shop, among other retailers, has responded to the growing interest in THCP by offering a variety of THCP-infused products, including gummies. These products provide a discreet and accessible way to explore the effects of THCP, catering to both recreational and therapeutic users looking for potent alternatives to traditional THC products.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The legal status of THC-P remains complex and varies by jurisdiction. As a compound derived from cannabis, THC-P falls into a legal gray area in many regions. Its potent psychoactive effects and potential therapeutic benefits make it a subject of interest for both policymakers and the scientific community. Consumers interested in THC-P products are advised to stay informed about local laws and regulations to navigate this evolving legal landscape responsibly.
Conclusion
THC-P represents a significant focus of current cannabinoid research, offering insights into the potential of cannabis beyond the well-known effects of Δ9-THC. As scientific understanding of THC-P expands, it holds promise for contributing to new therapeutic approaches and deepening our comprehension of cannabis’s pharmacological effects. Ongoing research into THC-P and its interactions with the endocannabinoid system is crucial for unlocking its full spectrum of benefits and applications, underscoring the importance of continued investigation into this and other cannabinoids.
